Kidney diseases can cause different degrees of kidney dysfunction. The kidney function can range from 100% (KF = 1) in patients with normal kidney function to 0% (KF = 0) in anureic patients
The kidney function can be determined by comparing the creatinine clearance of the patient with the normal .
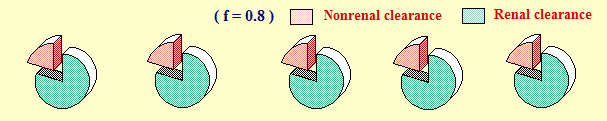
Consider this drug which is eliminated by renal (80%) and nonrenal (20%) elimination pathways (f = 0.8).
Assume that this drug was administered to a group of patients who have different kidney functions ranging from 1.0 to 0.1 (i.e. 100% to 10% of normal kidney function).
When the of the patient is 80% (KF=0.8) of normal, the of the drug will be 80% of normal renal clearance. This means that the in this patient will be the sum of the nonrenal clearance and 0.8 of the normal renal clearance.
On the other hand when the is 10% (KF=0.1) of normal, the of the drug will be 10% of normal renal clearance. The in this case will be the sum of the nonrenal clearance and 0.1 of the normal renal clearance.
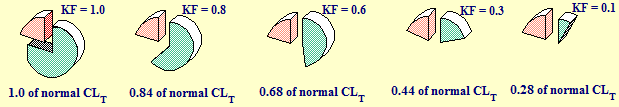
Lower kidney function results in a proportional decrease in the rate of renal elimination and the renal clearance of the drug. This will be reflected on the total body clearance of the drug.


